Data security is crucial to keep organizations safe from cybersecurity threats like data phishing. Let’s dive deeper to understand how data phishing poses a threat to your donors, members, and key stakeholders.
According to Verizon’s 2019 Data Breach Investigation Report, 94% of malware was delivered via email. In 2019, nearly 88% organizations across the globe experienced spear phishing attempts whereas 86% faced business email compromise (BEC) attempts. 65% of organizations in the USA fell victim to successful phishing attacks.
Data Phishing is a social engineering attack aimed at stealing sensitive user data, like credit card details or login credentials by the attacker masking as a reliable entity or person. The attacker uses text or
instant messages, and emails, prompting the recipient to click on a link or enter sensitive information and then steal data by infiltrating malware on the target’s device.
Data phishing amounted to 22% breaches in 2019 as per Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigation Report.
Check out a few ways you can protect your member and donor data in Salesforce.
- Monitor and audit employee and member accounts
- Implementing SPAM filter on email domain
- Implementing Security Infrastructure (Layer)
- Train your staff not to open suspicious emails and stay vigilant
- Monitor login activities and set real-time alerts
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) guarding access to your network
- Deploy a robust and trusted security system
- Enhancing digital security
- Verify accounts using U2F Security Keys
- Prevent domain spoofing in Salesforce
1. Monitor And Audit Employee And Member Accounts
Users and members who have been victims to such attacks in the past get their systems actively monitored and logs analyzed by their IT admins for any kind of security breach. Salesforce systems are monitored and audited to get system usage information that helps diagnose potential and real security threats. Conducting frequent audits through the Salesforce auditing feature can prevent such abuses. Setting session and transaction security restrictions prevents phishing attacks.
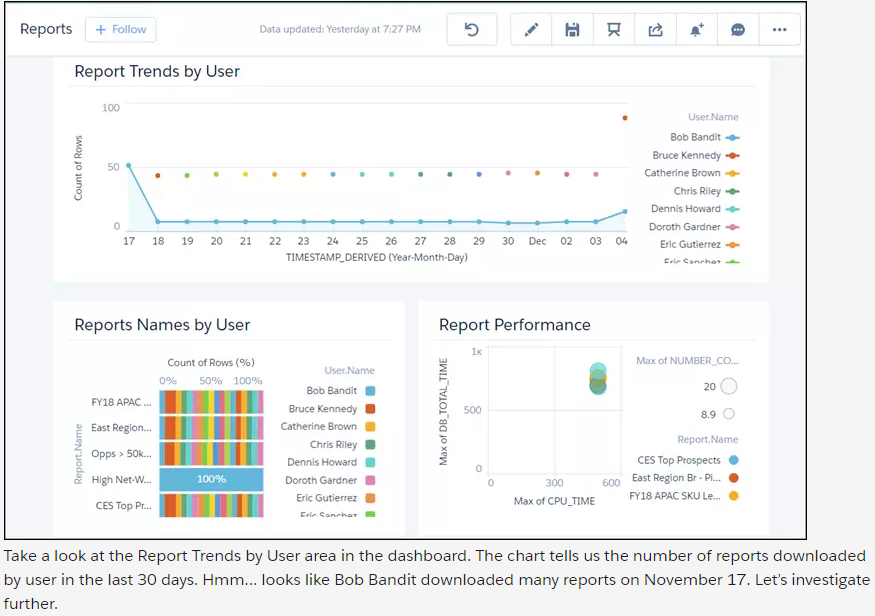
2. Implementing SPAM Filter On Email Domain
Make sure that your email administrator implements filters to prevent malicious mails from hitting staff’s email inbox. A cloud-based email service can act as a buffer. Your phishing protection system
should cover all your devices, allowing you to control settings through a simple UI that admins can easily watch over
Step 1.
- Go to the ‘Setup’ page -> click ‘Settings’ and then ‘Account Settings’
- ‘Account Settings’ -> ‘Edit’
- ‘General Settings’ -> fill in the email address under ‘Email Reply Address’
- Press ‘Verify’ -> ‘Save’ (if using authenticated domain, i.e. Private Domain or Sender
Authentication Package (SAP)) - If domains don’t match, send a verification email to the address and wait until the status button
turns to ‘Verify’ (almost 48 hours). Then hit the button to complete verification.
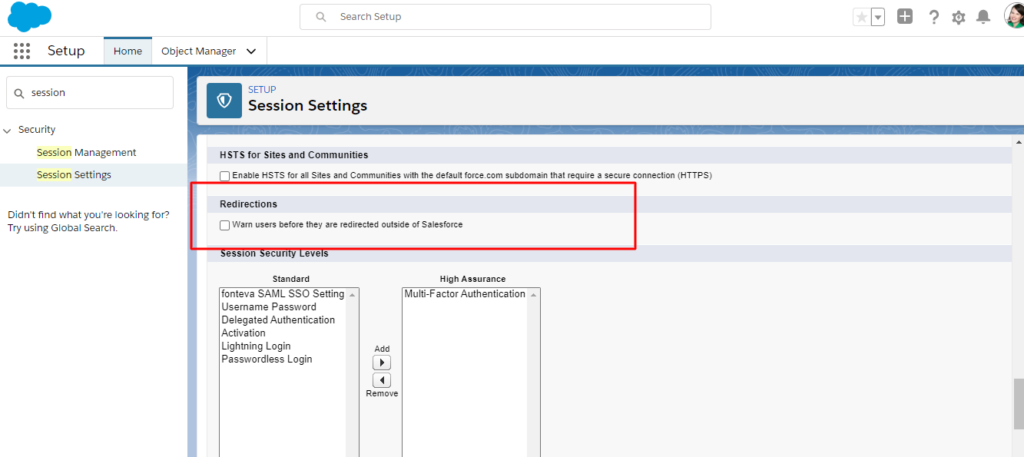
Step 2. Enabling redirects for trusted URLs:
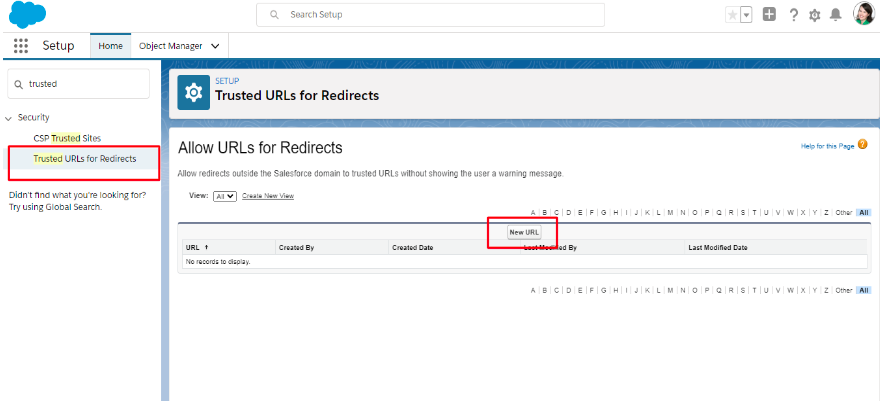
- Tap ‘Setup’ -> Quick Find box -> ‘Trusted URLs for Redirects’
- Hit ‘Trusted URLs for Redirects’ -> ‘New URL’ -> Enter the
URL
3. Implementing Security Infrastructure (Layer)
Implementing security layers is not a one-time approach. Salesforce provides you with applications through Salesforce-supported browsers, server authentication, and Classic Encryption in Transport Layer
Security (TLS) technology for information protection. These layers ensure organizational data security, safety, and accessibility dedicatedly for registered users. For example, locking your home with a
digital lock embedded with an app in addition to the existing physical locks. Now if someone tries to break the security system, it alerts you about the wrong passcode.
Authorizing Access
1. Request an authorization code
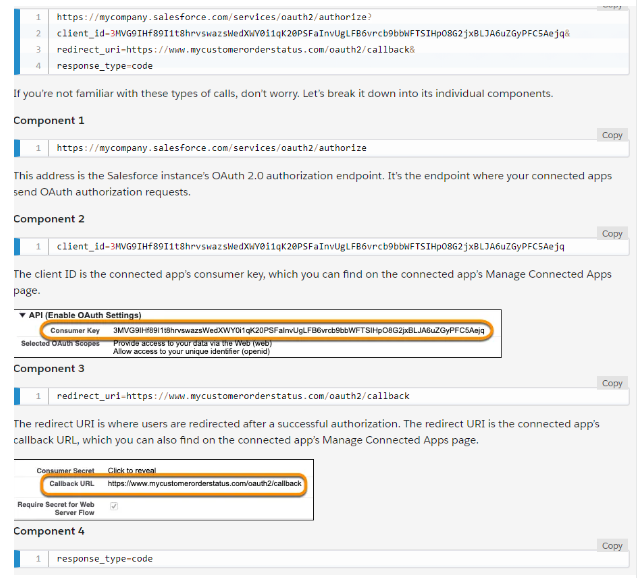
2. User authenticates and authorizes access
Click ‘Allow’ after you login
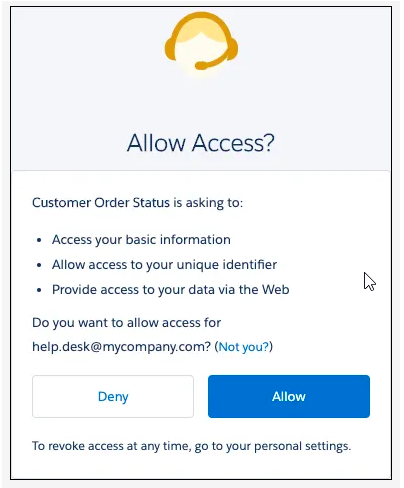
- Salesforce grants an authorization access code
- Request an access token
- Salesforce grants an access token
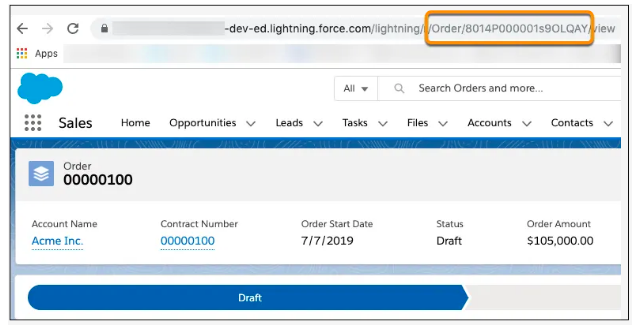
Example of Access token received from the server to access order data:
4. Train Your Staff Not To Open Suspicious Emails And Stay Vigilant
Train employees on zero-trust concepts to stay alert and recognize red-flags, suspicious looking emails, unusual addresses, communications, etc. Tips to provide staff:
- Don’t open emails or attachments from unknown sources.
- Don’t share passwords, OTPs (One Time Password), or SSN (Social Security Numbers) details.
- When people are about to click on the link, they should hover the mouse over it to check the destination of the link for ensuring that they are being redirected to an authentic page (the official page they are supposed to visit) to carry out any desired task. Hover the cursor over embedded links to see the destination URL displayed at the left hand side on the screen.
- Be aware of messages with poor graphics, typos, unbelievable rewards, and threats.
- Verify questionable internal emails by reaching out to departments. One common example of potential phishing: emails masquerading as your CEO are being sent from the finance department for money transfer and look very real. Reach out to your HR or finance department – even before clicking on the email.
5. Monitor Login Activities And Set Real-Time Alerts
Numerous logins happen across the organization throughout the day every hour. Determining which user account(s) were compromised can be a difficult task. Salesforce login forensics can identify the dubious login activities with key user data including average logins per user at a particular time, non-business hour logins, users exceeding average logins, and logins through suspicious IPs. For instance, if you encounter any login episodes from any employee’s ID that do not seem to be genuine (because of irregular timings or suspected location), there might be a security breach issue.
Salesforce’s Identity and Access Management (IAM) platform also plays a crucial role here. Through IAM, you can monitor policies and tools as well as ensure that your employees are logging in/accessing their respective data from genuine or respective locations, at fixed locations and at reasonable timings. Salesforce Identity can be of use in case you already don’t have an IAM for your IT ecosystem.
6. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Guarding Access To Your Network
MFA secures your organization from data phishing, account takeovers, and credential stuffing threats as well. Salesforce admins add this additional layer of security to user and member logins – so that users need to meet specific criteria for accessing sensitive reports and connected apps within your Salesforce ecosystem. MFA or 2FA means you need an one-time password (OTP) (by email or sms) or biometric verification along with the usual password for your account.
7. Deploy A Robust And Trusted Security System
To ensure malware and spam protection, a security system is essential for your organization that adds email filters, and scans attachments and hyperlinks. Security tools like Salesforce Shield enable admins and developers to build additional security features for compliance, trust, and governance for crucial business applications.
- Setting IP range restrictions for the Salesforce system allows access only through your corporate network and VPN.
8. Enhance Digital Security
The Salesforce Administration should keep all your systems updated with the latest security patches on your devices. Monitoring antivirus status should be a regular activity on all equipment. Opting for
saving data in encrypted formats and deploying a web filter is an effective way to block malicious websites and cyberattacks.
9. Verify Accounts Using U2F Security Keys
When users can’t verify their identity through device activation or MFA, enable them to use Universal Second Factor (U2F) security key. The verification gets seamlessly done by entering the U2F security key in the desired device port for a successful verification.
Here are the steps:
- Go to ‘Setup’ -> on Quick Find box enter ‘Session Settings’ -> select ‘Session Settings’
- Choose ‘Let users verify their identity with a physical security key (U2F)’
- ‘Save’ the changes
* Enable ‘My Domain’ before enabling the U2F key.
10. Prevent Domain Spoofing in Salesforce
Domain spoofing protection is important to shield your online reputation. Deploying Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) allows you to authenticate emails and senders to ensure recipients are getting those emails from legitimate sources. DMARC helps stop phishing emails prior to reaching the users, gives real-time alerts about phishing attempts, and lowers the risk of phishing emails entering your organization. Email server authentication is also a secure method to prevent spoofing and phishing attacks.
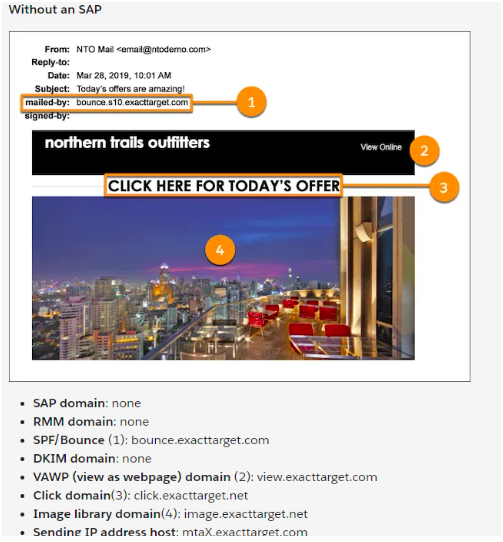
Emails Without a Sender Authentication Package (SAP) for Domain-based Message Authentication
Emails With SAP
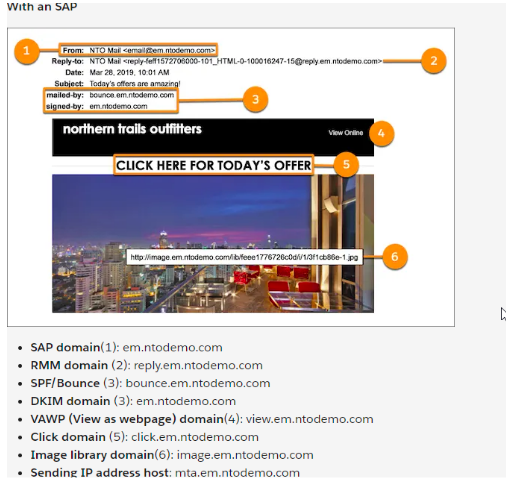
SAP helps users identify good email senders and the bad senders.
With trusted Salesforce managed services, there is hardly any risk of putting your nonprofit and association in any kind of online security related trouble. Managed Salesforce providers ensure nonprofits and associations to help them have a connected, efficient, affordable, and productive ecosystem tightly secured from cyberattacks and fulfil their members’ requirements using the right technology. Salesforce-certified experts understand your organization’s security requirements like no one else. If you are looking forward to minimizing staff time, improving technical capabilities, without falling prey to phishing attacks – contact us today to stay secure for as low as $60/hour.
Resources
- Phishing Facts | Statistics on Phishing and other Cyber Threats
- 2019 Phishing Statistics and Email Fraud Statistics
- 3 Tips to Avoid Phishing Scams
- Verizon 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report

